Description Link to heading
- Maximal Rectangle (Hard)
Given a
rows x colsbinarymatrixfilled with0’s and1’s, find the largest rectangle containing only1’s and return its area.
Example 1:
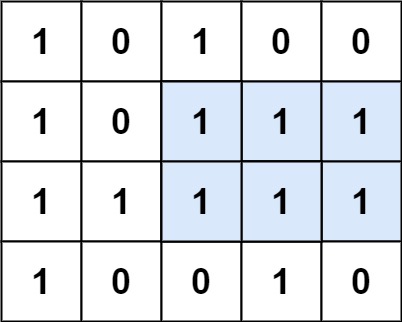
Input: matrix =
[["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0","1","1","1"],["1","1","1","1","1"],["1","0","0","1","0"]]
Output: 6
Explanation: The maximal rectangle is shown in the above picture.
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [["0"]]
Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: matrix = [["1"]]
Output: 1
Constraints:
rows == matrix.lengthcols == matrix[i].length1 <= row, cols <= 200matrix[i][j]is'0'or'1'.
Solution Link to heading
In essence, this problem is akin to a layer encapsulating 84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram (Hard). Once this point is realized, the problem becomes less challenging.
Code Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &heights) {
if (heights.size() == 1) {
return heights[0];
}
stack<int> stk;
int n = heights.size();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while (!stk.empty() && heights[i] < heights[stk.top()]) {
int h = heights[stk.top()];
stk.pop();
if (!stk.empty()) {
res = max(res, (i - stk.top() - 1) * h);
} else {
res = max(res, (i)*h);
}
}
stk.push(i);
}
int right = stk.top();
while (!stk.empty()) {
int h = heights[stk.top()];
stk.pop();
if (!stk.empty()) {
res = max(res, (right - stk.top()) * h);
} else {
res = max(res, h * n);
}
}
return res;
}
};