Description Link to heading
84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram (Hard)
Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each
bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
Example 1:
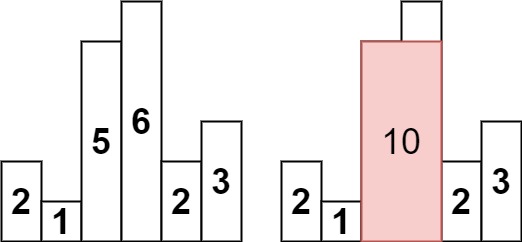
Input: heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
Output: 10
Explanation: The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1.
The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
Example 2:
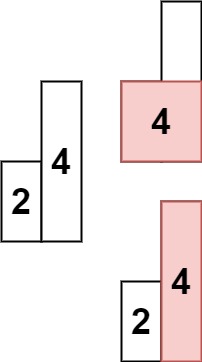
Input: heights = [2,4]
Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= heights.length <= 10⁵0 <= heights[i] <= 10⁴
Solution Link to heading
Indeed, this problem essentially seeks the minimum value within a variable length, continuous interval, as well as the length of this interval. The employment of a monotonic stack could be considered for this purpose. Whether to utilize a monotonically increasing or decreasing stack can be determined by simulating the examples provided in the problem statement. In this case, a monotonically increasing stack (from bottom to top) should be used.
In this problem, we traverse the array. For nums[i], we identify the smallest r (denoted as ridx) that satisfies nums[r] < nums[i] and r > i, and the largest l (denoted as lidx) that satisfies nums[l] < nums[i] and l < i. Therefore, res = max(res, nums[i] * (ridx - lidx - 1)). We can utilize a monotonic stack to solve this problem within a time complexity of $O(n)$.
Code Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &heights) {
if (heights.size() == 1) {
return heights[0];
}
stack<int> stk;
int n = heights.size();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while (!stk.empty() && heights[i] < heights[stk.top()]) {
int h = heights[stk.top()];
stk.pop();
if (!stk.empty()) {
res = max(res, (i - stk.top() - 1) * h);
} else {
res = max(res, (i)*h);
}
}
stk.push(i);
}
int right = stk.top();
while (!stk.empty()) {
int h = heights[stk.top()];
stk.pop();
if (!stk.empty()) {
res = max(res, (right - stk.top()) * h);
} else {
res = max(res, h * n);
}
}
return res;
}
};