Description Link to heading
778. Swim in Rising Water (Hard)
You are given an n x n integer matrix grid where each value grid[i][j] represents the
elevation at that point (i, j).
The rain starts to fall. At time t, the depth of the water everywhere is t. You can swim from a
square to another 4-directionally adjacent square if and only if the elevation of both squares
individually are at most t. You can swim infinite distances in zero time. Of course, you must stay
within the boundaries of the grid during your swim.
Return the least time until you can reach the bottom right square (n - 1, n - 1) if you start at
the top left square (0, 0).
Example 1:
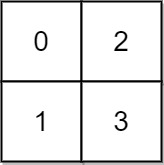
Input: grid = [[0,2],[1,3]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
At time 0, you are in grid location (0, 0).
You cannot go anywhere else because 4-directionally adjacent neighbors have a higher elevation than
t = 0.
You cannot reach point (1, 1) until time 3.
When the depth of water is 3, we can swim anywhere inside the grid.
Example 2:
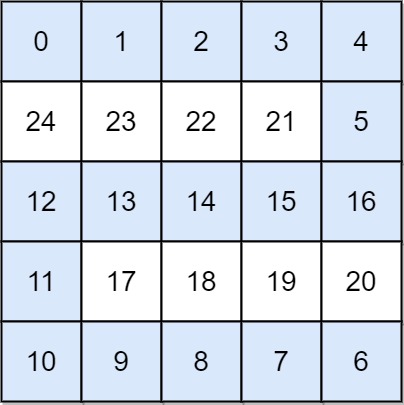
Input: grid = [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]]
Output: 16
Explanation: The final route is shown.
We need to wait until time 16 so that (0, 0) and (4, 4) are connected.
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] < n²- Each value
grid[i][j]is unique.
Solution Link to heading
binary search + bfs Link to heading
We can use binary search to find the answer. We will wait mid time first:
- if we can reach the destination, it means
mid >= ans, thenright = mid; - otherwise,
mid < ans, thenleft = mid + 1
dijkstra Link to heading
We push std::max(time, grid[i][j]) into the pq.
Code Link to heading
binary search + bfs Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
bool bfs(vector<vector<int>> &grid, int mid) {
int n = grid.size();
vector<vector<int>> vis(n, vector<int>(n, 0));
queue<vector<int>> q;
q.push({0, 0});
vis[0][0] = 1;
vector<vector<int>> mov{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
while (!q.empty()) {
auto vec = q.front();
if (vec[0] == n - 1 && vec[1] == n - 1) {
return true;
}
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int x_new = vec[0] + mov[i][0], y_new = vec[1] + mov[i][1];
if (x_new >= 0 && x_new < n && y_new >= 0 && y_new < n && vis[x_new][y_new] == 0 && mid >= grid[x_new][y_new]) {
q.push({x_new, y_new});
vis[x_new][y_new] = 1;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int swimInWater(vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
int left = 0, right = 2500;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (bfs(grid, mid)) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return std::max(left, grid[0][0]);
}
};
dijkstra Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
int swimInWater(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
auto cmp = [&](vector<int> &v1, vector<int> &v2) {
return v1[2] > v2[2];
};
priority_queue<vector<int> , vector<vector<int>>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp);
pq.push({0, 0, grid[0][0]});
vector<vector<int>> dis(n, vector<int>(n, -1));
vector<vector<int>> mov{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto vec = pq.top();
int x = vec[0], y = vec[1], time = vec[2];
pq.pop();
if (dis[x][y] != -1) {
continue;
}
dis[x][y] = time;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int new_x = x + mov[i][0], new_y = y + mov[i][1];
if (new_x >= 0 && new_x < n && new_y >= 0 && new_y < n) {
if (dis[new_x][new_y] == -1) {
if (time >= grid[new_x][new_y]) {
pq.push({new_x, new_y, time});
} else {
pq.push({new_x, new_y, grid[new_x][new_y]});
}
}
}
}
}
return dis[n - 1][n - 1];
}
};