Description Link to heading
654. Maximum Binary Tree (Medium)
You are given an integer array nums with no duplicates. A maximum binary tree can be built
recursively from nums using the following algorithm:
- Create a root node whose value is the maximum value in
nums. - Recursively build the left subtree on the subarray prefix to the left of the maximum value.
- Recursively build the right subtree on the subarray suffix to the right of the maximum value.
Return the maximum binary tree built from nums.
Example 1:
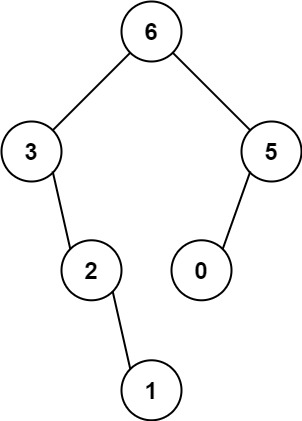
Input: nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5]
Output: [6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1]
Explanation: The recursive calls are as follow:
- The largest value in [3,2,1,6,0,5] is 6. Left prefix is [3,2,1] and right suffix is [0,5].
- The largest value in [3,2,1] is 3. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [2,1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- The largest value in [2,1] is 2. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 1.
- The largest value in [0,5] is 5. Left prefix is [0] and right suffix is [].
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 0.
- Empty array, so no child.
Example 2:
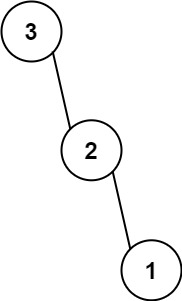
Input: nums = [3,2,1]
Output: [3,null,2,null,1]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 1000- All integers in
numsare unique.
Solution Link to heading
divide and conquer Link to heading
monotone stack Link to heading
Code Link to heading
divide and conquer Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *dfs(vector<int> &nums, int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) {
return nullptr;
}
int val = nums[l], idx = l;
for (int i = l; i < r; ++i) {
if (nums[i] > val) {
val = nums[i];
idx = i;
}
}
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(val, dfs(nums, l, idx), dfs(nums, idx + 1, r));
return root;
}
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
return dfs(nums, 0, nums.size());
}
};
monotone stack Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int> &nums) {
// 尝试使用单调栈
stack<TreeNode *> stk;
stack<TreeNode *> tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
while (!stk.empty() && nums[i] > stk.top()->val) {
tmp.push(stk.top());
stk.pop();
}
TreeNode *node = new TreeNode(nums[i]);
TreeNode *p = node;
int flag = 0;
while (!tmp.empty()) {
if (flag == 0) {
p->left = tmp.top();
p = p->left;
} else {
p->right = tmp.top();
p = p->right;
}
++flag;
tmp.pop();
}
stk.push(node);
}
TreeNode *root;
while (!stk.empty()) {
tmp.push(stk.top());
stk.pop();
if (!stk.empty()) {
stk.top()->right = tmp.top();
}
}
return tmp.top();
}
};