Description Link to heading
407. Trapping Rain Water II (Hard)
Given an m x n integer matrix heightMap representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D
elevation map, return the volume of water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:
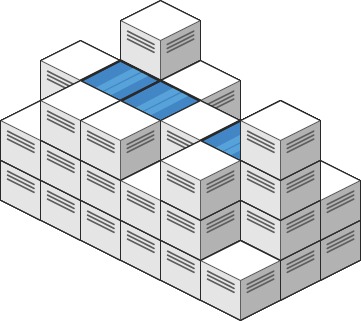
Input: heightMap = [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks.
We have two small ponds 1 and 3 units trapped.
The total volume of water trapped is 4.
Example 2:
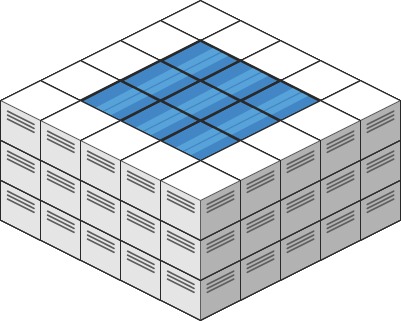
Input: heightMap = [[3,3,3,3,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,2,1,2,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,3,3,3,3]]
Output: 10
Constraints:
m == heightMap.lengthn == heightMap[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heightMap[i][j] <= 2 * 10⁴
Solution Link to heading
We can use the Dijkstra algorithm to find the maximum height $h_xy$ in the path from the point $(x, y)$ in the edge to the point $(i, j)$.
The volume of water of each cell is $\min(h_{x, y})^{i, j} - heightMap[i][j]$
Code Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>> &heightMap) {
int m = heightMap.size();
int n = heightMap[0].size();
auto cmp = [&](vector<int> &v1, vector<int> &v2) {
return v1[2] > v2[2];
};
priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
pq.push({0, i, heightMap[0][i]});
pq.push({m - 1, i, heightMap[m - 1][i]});
}
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; ++i) {
pq.push({i, 0, heightMap[i][0]});
pq.push({i, n - 1, heightMap[i][n - 1]});
}
vector<vector<int>> dis(m, vector<int>(n));
vector<vector<int>> vis(m, vector<int>(n));
vector<vector<int>> neighbor{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto vec = pq.top();
int x = vec[0], y = vec[1], height = vec[2];
pq.pop();
if (vis[x][y] != 0) {
continue;
}
vis[x][y] = 1;
dis[x][y] = height;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int new_x = x + neighbor[i][0];
int new_y = y + neighbor[i][1];
if (new_x < m && new_x >= 0 && new_y < n && new_y >= 0) {
pq.push({new_x, new_y, std::max(height, heightMap[new_x][new_y])});
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; ++j) {
res += dis[i][j] - heightMap[i][j];
}
}
return res;
}
};