Description Link to heading
373. Find K Pairs with Smallest Sums (Medium)
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2 sorted in ascending order and an integer
k.
Define a pair (u, v) which consists of one element from the first array and one element from the
second array.
Return the kpairs (u₁, v₁), (u₂, v₂), ..., (uₖ, vₖ)with the smallest sums.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,7,11], nums2 = [2,4,6], k = 3
Output: [[1,2],[1,4],[1,6]]
Explanation: The first 3 pairs are returned from the sequence:
[1,2],[1,4],[1,6],[7,2],[7,4],[11,2],[7,6],[11,4],[11,6]
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1,1,2], nums2 = [1,2,3], k = 2
Output: [[1,1],[1,1]]
Explanation: The first 2 pairs are returned from the sequence:
[1,1],[1,1],[1,2],[2,1],[1,2],[2,2],[1,3],[1,3],[2,3]
Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3], k = 3
Output: [[1,3],[2,3]]
Explanation: All possible pairs are returned from the sequence: [1,3],[2,3]
Constraints:
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 10⁵-10⁹ <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 10⁹nums1andnums2both are sorted in ascending order.1 <= k <= 10⁴
Solution Link to heading
Firstly, a min-heap can be used to obtain the smallest pair of numbers each time. Assuming that the current smallest pair is $(a_i, b_j)$, there may be two pairs that are larger but still the smallest: $(a_{i+1}, b_j)$ and $(a_i, b_{j+1})$. However, directly adding these pairs to the queue may result in duplicate pairs being selected. To solve this problem, you can refer to the following two diagrams:
In case of duplicate pairs:
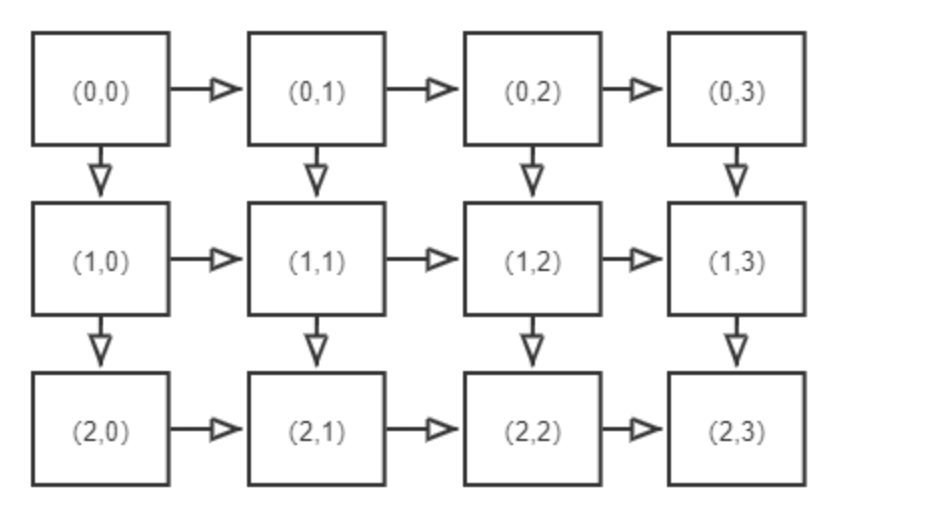
To remove duplicates:
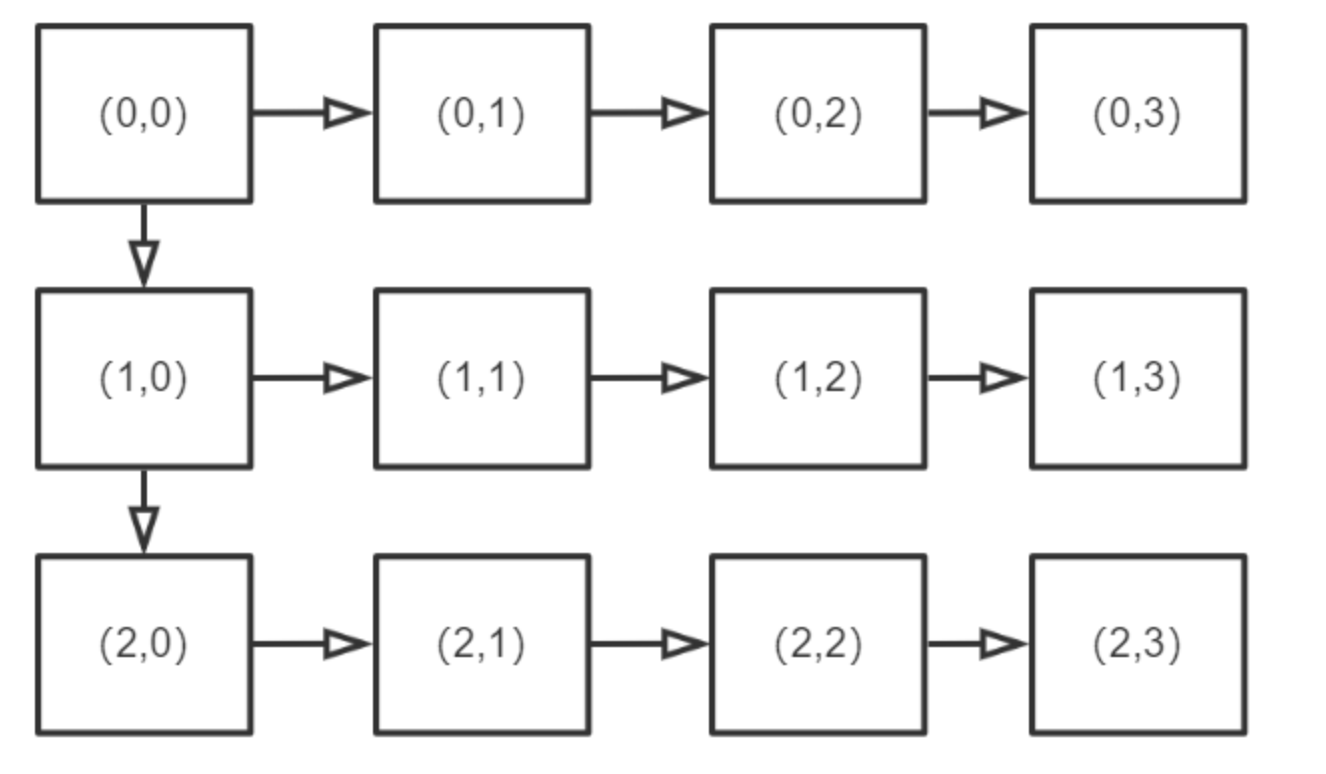
Code Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> kSmallestPairs(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, int k) {
auto cmp = [&nums1, &nums2](const pair<int, int> & a, const pair<int, int> & b) {
return nums1[a.first] + nums2[a.second] > nums1[b.first] + nums2[b.second];
};
int m = nums1.size();
int n = nums2.size();
vector<vector<int>> ans;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < min(k, m); i++) {
pq.emplace(i, 0);
}
while (k-- > 0 && !pq.empty()) {
auto [x, y] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
ans.emplace_back(initializer_list<int>{nums1[x], nums2[y]});
if (y + 1 < n) {
pq.emplace(x, y + 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
};