Description Link to heading
2584. Split the Array to Make Coprime Products (Hard)
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums of length n.
A split at an index i where 0 <= i <= n - 2 is called valid if the product of the first
i + 1 elements and the product of the remaining elements are coprime.
- For example, if
nums = [2, 3, 3], then a split at the indexi = 0is valid because2and9are coprime, while a split at the indexi = 1is not valid because6and3are not coprime. A split at the indexi = 2is not valid becausei == n - 1.
Return the smallest index i at which the array can be split validly or -1 if there is no such
split.
Two values val1 and val2 are coprime if gcd(val1, val2) == 1 where gcd(val1, val2) is the
greatest common divisor of val1 and val2.
Example 1:
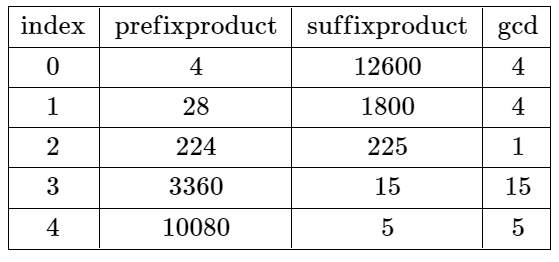
Input: nums = [4,7,8,15,3,5]
Output: 2
Explanation: The table above shows the values of the product of the first i + 1 elements, the
remaining elements, and their gcd at each index i.
The only valid split is at index 2.
Example 2:
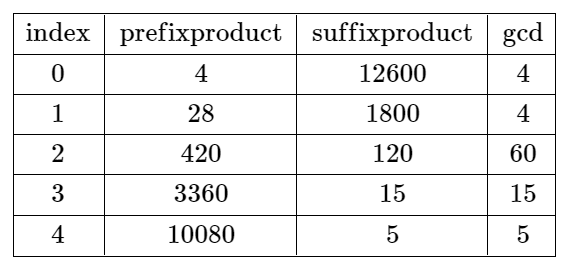
Input: nums = [4,7,15,8,3,5]
Output: -1
Explanation: The table above shows the values of the product of the first i + 1 elements, the
remaining elements, and their gcd at each index i.
There is no valid split.
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 10⁴1 <= nums[i] <= 10⁶
Solution Link to heading
Partitioning the array so that the products are mutually prime is essentially letting the numbers on the left and right halves contain different prime factors from each other. Consider the prime factor $i$, i.e., find the indexes of the leftmost and rightmost numbers whose prime factors contain $i$, which then translates into the interval overlap problem.
Code Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
void get_range(int fac, int idx, unordered_map<int, pair<int, int>> &factor_range) {
if (factor_range.find(fac) != factor_range.end()) {
factor_range[fac].second = idx;
} else {
factor_range[fac] = {idx, idx};
}
}
int findValidSplit(vector<int> &nums) {
if (nums.size() < 2)
return -1;
unordered_map<int, pair<int, int>> factor_range;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
for (int fac = 2; fac * fac <= nums[i]; fac++) {
if (nums[i] % fac == 0) {
while (nums[i] % fac == 0) {
nums[i] /= fac;
}
get_range(fac, i, factor_range);
}
}
if (nums[i] > 1) { // 说明nums[i]本身是质数
get_range(nums[i], i, factor_range);
}
}
vector<pair<int, int>> factors;
factors.reserve(factor_range.size());
for (auto &range : factor_range) {
factors.push_back(range.second);
}
std::sort(factors.begin(), factors.end());
int left = factors[0].first;
int right = factors[0].second;
for (int i = 1; i < factors.size(); i++) {
if (factors[i].first > right) {
return factors[i].first - 1;
} else {
right = std::max(factors[i].second, right);
}
}
return -1;
}
};