Solution Link to heading
1631. Path With Minimum Effort (Medium)
You are a hiker preparing for an upcoming hike. You are given heights, a 2D array of size rows x columns, where heights[row][col] represents the height of cell (row, col). You are situated in
the top-left cell, (0, 0), and you hope to travel to the bottom-right cell, (rows-1, columns-1)
(i.e., 0-indexed). You can move up, down, left, or right, and you wish to find a
route that requires the minimum effort.
A route’s effort is the maximum absolute difference in heights between two consecutive cells of the route.
Return the minimum effort required to travel from the top-left cell to the bottom-right cell.
Example 1:
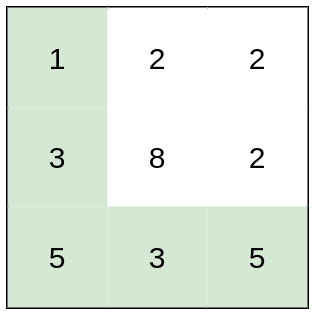
Input: heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The route of [1,3,5,3,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 2 in consecutive cells.
This is better than the route of [1,2,2,2,5], where the maximum absolute difference is 3.
Example 2:
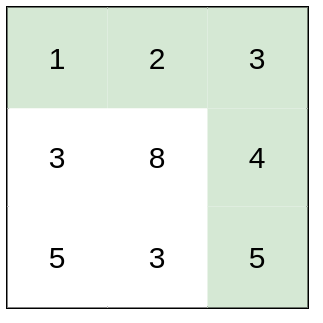
Input: heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]]
Output: 1
Explanation: The route of [1,2,3,4,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 1 in consecutive cells,
which is better than route [1,3,5,3,5].
Example 3:
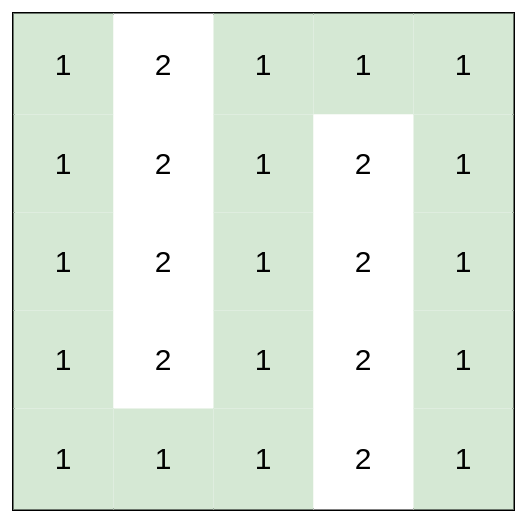
Input: heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]]
Output: 0
Explanation: This route does not require any effort.
Constraints:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 10⁶
Solution Link to heading
Dijkstra algorithm Link to heading
We can use Dijkstra algorithm to find the answer.
binary search Link to heading
Code Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>> &heights) {
int m = heights.size(), n = heights[0].size();
// Dijkstra
auto cmp = [&](vector<int> &v1, vector<int> &v2) {
return v1[2] > v2[2];
};
priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp);
vector<vector<int>> dis(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
vector<vector<int>> move{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
pq.push({0, 0, 0});
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto vec = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int x = vec[0], y = vec[1], cost = vec[2];
if (dis[x][y] != -1) {
continue;
}
dis[x][y] = cost;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int new_x = x + move[i][0];
int new_y = y + move[i][1];
if (new_x >= 0 && new_x < m && new_y >= 0 && new_y < n) {
if (dis[new_x][new_y] == -1) {
pq.push({new_x, new_y, std::max(cost, abs(heights[x][y] - heights[new_x][new_y]))});
}
}
}
}
return dis[m - 1][n - 1];
}
};