Description Link to heading
1615. Maximal Network Rank (Medium)
There is an infrastructure of n cities with some number of roads connecting these cities. Each
roads[i] = [aᵢ, bᵢ] indicates that there is a bidirectional road between cities aᵢ and bᵢ.
The network rank of two different cities is defined as the total number of directly connected roads to either city. If a road is directly connected to both cities, it is only counted once.
The maximal network rank of the infrastructure is the maximum network rank of all pairs of different cities.
Given the integer n and the array roads, return the maximal network rank of the entire
infrastructure.
Example 1:

Input: n = 4, roads = [[0,1],[0,3],[1,2],[1,3]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The network rank of cities 0 and 1 is 4 as there are 4 roads that are connected to
either 0 or 1. The road between 0 and 1 is only counted once.
Example 2:
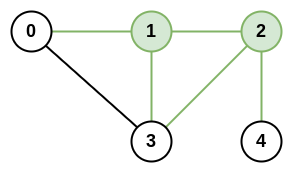
Input: n = 5, roads = [[0,1],[0,3],[1,2],[1,3],[2,3],[2,4]]
Output: 5
Explanation: There are 5 roads that are connected to cities 1 or 2.
Example 3:
Input: n = 8, roads = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[2,4],[5,6],[5,7]]
Output: 5
Explanation: The network rank of 2 and 5 is 5. Notice that all the cities do not have to be
connected.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1000 <= roads.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2roads[i].length == 20 <= aᵢ, bᵢ <= n-1aᵢ != bᵢ- Each pair of cities has at most one road connecting them.
Solution Link to heading
We can use a adjacent matrix to store the graph, to determine whether two points are connected directly. When creating the adjacent matrix, we need to record the number of points which are directly connected with the current point. And then traverse the points.
Code Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
int maximalNetworkRank(int n, vector<vector<int>> &roads) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(n, vector<int>(n));
vector<int> cnt(n);
for (auto &vec : roads) {
graph[vec[0]][vec[1]] = 1;
cnt[vec[0]]++;
graph[vec[1]][vec[0]] = 1;
cnt[vec[1]]++;
}
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (graph[i][j] == 1) {
num = std::max(num, cnt[i] + cnt[j] - 1);
} else {
num = std::max(num, cnt[i] + cnt[j]);
}
}
}
return num;
}
};