Description Link to heading
1326. Minimum Number of Taps to Open to Water a Garden (Hard)
There is a one-dimensional garden on the x-axis. The garden starts at the point 0 and ends at the
point n. (i.e The length of the garden is n).
There are n + 1 taps located at points [0, 1, ..., n] in the garden.
Given an integer n and an integer array ranges of length n + 1 where ranges[i] (0-indexed)
means the i-th tap can water the area [i - ranges[i], i + ranges[i]] if it was open.
Return the minimum number of taps that should be open to water the whole garden, If the garden cannot be watered return -1.
Example 1:
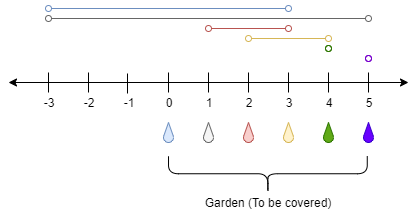
Input: n = 5, ranges = [3,4,1,1,0,0]
Output: 1
Explanation: The tap at point 0 can cover the interval [-3,3]
The tap at point 1 can cover the interval [-3,5]
The tap at point 2 can cover the interval [1,3]
The tap at point 3 can cover the interval [2,4]
The tap at point 4 can cover the interval [4,4]
The tap at point 5 can cover the interval [5,5]
Opening Only the second tap will water the whole garden [0,5]
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, ranges = [0,0,0,0]
Output: -1
Explanation: Even if you activate all the four taps you cannot water the whole garden.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10⁴ranges.length == n + 10 <= ranges[i] <= 100
Solution Link to heading
Dynamic programming Link to heading
We represent dp[i] as the least amount of taps to cover [0, i].
Assuming that the coverage of the last tap is [start[i], end[j]], then for start[j] < k < end[j], dp[k] = min(dp[k], dp[start[j]] + 1), so we need to initialize dp[i] as very large values, and sort the water_range array by start[i] from small to large.
Sort + Binary Search Link to heading
Greey algorithm: Suppose the rightmost end that can be watered is end and the corresponding tap is start_idx, then the i that satisfies start[i] <= end and end[i] is the largest i should be selected, we can find the maximum idx of i that satisfies start[i] <= end by using dichotomous search, then traverse [start_idx, idx] to find the largest end[i] and update start_idx.
Greedy algorithm Link to heading
Suppose the rightmost end that can be watered is end and the corresponding tap is start_idx, then the i that satifies start[i] <= end and end[i] is the largest should be selected. We use an array vector<int> right_most(n + 1, 0) that represents the farthest point that can be watered when the point with coordinate i can be watered.
Then, we traverse i from 0 to n, and if right_most[i] is greater than next_right, then update next_right, and the original next_right is recorded as cur_right, and if i == cur_right now, it means that another tap has to be opened.
Code Link to heading
Dynamic programming Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
int minTaps(int n, vector<int> &ranges) {
vector<vector<int>> water_range;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
water_range.push_back({std::max(0, i - ranges[i]), std::min(i + ranges[i], n)});
}
std::sort(water_range.begin(), water_range.end());
vector<int> dp(n + 1, 30000);
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (dp[water_range[i][0]] == 30000)
return -1;
for (int j = water_range[i][0]; j <= water_range[i][1]; j++) {
dp[j] = std::min(dp[j], dp[water_range[i][0]] + 1);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};
Sort + Binary search Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
// binary search
int Bfind(vector<vector<int>> &vec, int target, int start_idx) {
int left = start_idx, right = vec.size();
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
while (left < right) {
if (vec[mid][0] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
}
return left;
}
int minTaps(int n, vector<int> &ranges) {
vector<vector<int>> water_range;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
water_range.push_back({i - ranges[i], i + ranges[i]});
}
auto cmp = [&](vector<int> &v1, vector<int> &v2) {
if (v1[0] == v2[0])
return v1[1] <= v2[1];
return v1[0] < v2[0];
};
std::sort(water_range.begin(), water_range.end(), cmp);
int start_idx = 0, end = 0;
int cnt = 0;
while (end < n) {
int idx = Bfind(water_range, end + 1, start_idx) - 1; // find greatest idx that satisfies start[idx] <= end
for (int i = start_idx; i <= idx; i++) {
if (water_range[i][1] > end) {
start_idx = i;
end = water_range[i][1];
}
}
cnt++;
if (cnt > n)
return -1;
}
return cnt;
}
};
Greedy algorithm Link to heading
class Solution {
public:
int minTaps(int n, vector<int> &ranges) {
int right_most[n + 1]; memset(right_most, 0, sizeof(right_most));
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
int r = ranges[i];
if (i > r) right_most[i - r] = i + r;
else right_most[0] = max(right_most[0], i + r);
}
int ans = 0;
int cur_right = 0;
int next_right = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
next_right = max(next_right, right_most[i]);
if (i == cur_right) {
if (i == next_right) return -1;
cur_right = next_right;
++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
};