Description Link to heading
1020. Number of Enclaves (Medium)
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid, where 0 represents a sea cell and 1 represents a
land cell.
A move consists of walking from one land cell to another adjacent ( 4-directionally) land
cell or walking off the boundary of the grid.
Return the number of land cells in gridfor which we cannot walk off the boundary of the grid in
any number of moves.
Example 1:
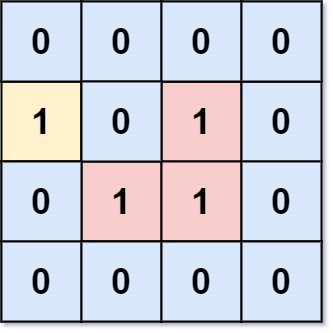
Input: grid = [[0,0,0,0],[1,0,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,0]]
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three 1s that are enclosed by 0s, and one 1 that is not enclosed because its
on the boundary.
Example 2:
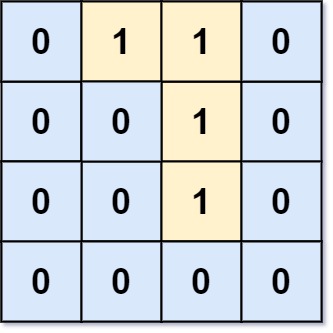
Input: grid = [[0,1,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,0]]
Output: 0
Explanation: All 1s are either on the boundary or can reach the boundary.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500grid[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution Link to heading
We can use dsu to solve this problem.
Code Link to heading
struct Dsu {
vector<int> par_;
vector<int> siz_;
int cnt_;
explicit Dsu(int cnt) :
par_(cnt + 1), siz_(cnt + 1, 1), cnt_(cnt) {
for (int i = 0; i <= cnt; ++i) {
par_[i] = i;
}
};
auto find(int x) -> int {
return par_[x] == x ? x : (par_[x] = find(par_[x]));
}
void uni(int x, int y) {
x = find(x), y = find(y);
if (x == y) {
return;
}
if (siz_[x] < siz_[y]) {
std::swap(x, y);
}
par_[y] = x;
siz_[x] += siz_[y];
--cnt_;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int numEnclaves(vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
// 并查集
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> move{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
Dsu dsu(m * n);
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m * n; ++i) {
int x = i / n, y = i % n;
if (grid[x][y] == 1) {
if (x == m - 1 || x == 0 || y == 0 || y == n - 1) {
dsu.uni(i, m * n);
}
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
int x_new = x + move[j][0], y_new = y + move[j][1];
if (x_new < 0 || x_new >= m || y_new < 0 || y_new >= n || grid[x_new][y_new] == 0) {
continue;
}
dsu.uni(i, x_new * n + y_new);
}
} else {
++cnt;
}
}
return m * n - dsu.siz_[dsu.find(m * n)] - cnt + 1;
}
};